Breast biopsy for diagnosis
How is breast cancer diagnosed?1,2
The process of setting a breast cancer diagnosis includes three steps: an examination, imaging and tissue sampling, where the final step is crucial.
- Breast examination. A doctor will check both breasts and lymph nodes in the armpit, feeling for any lumps or other abnormalities.
- Mammography or some other type of image diagnostics like ultrasound or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Other imaging methods may be used depending on the individual situation.
- The third and crucial step to arrive at a correct diagnosis is biopsy (tissue sampling).
Isn't mammography and ultrasound enough to make a diagnosis?
The doctor cannot determine if a lesion is benign or cancer only by a physical examination. Mammography and ultrasound are good methods, but they do not alone provide a reliable answer. To definitively diagnose breast cancer, analysis of tissue from the suspected area is needed.2
What is a breast biopsy?
A breast biopsy is a test performed to remove tissue or cells from a suspicious area in the breast and examine them under a microscope to check for the presence of breast cancer.3
Why are biopsies needed?
Breast biopsy is the only definitive diagnostic procedure that can determine if the suspicious area is cancerous. It is the only available method to diagnose breast cancer.2
To diagnose breast cancer with the help of biopsies also means to be able to4:
- Determine the type of cancer
- Determine the extent or size of the tumour
- Optimize individualized treatment regime
- Follow up the treatment and, if necessary, change treatment type
How is a breast biopsy performed?
Previously biopsies were performed surgically with an incision. Nowadays, breast biopsies are usually done by a radiologist using a less invasive procedure, involving a hollow needle aided by some image-guidance (for example ultrasound) to ensure that the sample is collected from the correct area.5
How is a breast biopsy analysed?
The test result is sent to a pathologist who analyses the tissue sample (tissue structure and cells) in a microscope.2 The pathologist and the microscopic tissue analysis have a central role in the diagnosis of cancer diseases.6
What will the pathologist look for in a tissue sample from the breast?
Current advances in oncology require a great deal of additional information both for prognosis and therapeutic intervention. The following details may all be relevant in the pathologic assessment of abnormal tissue growth:
- The type and origin of the tumour
- Its differentiation
- Level of invasion
- The numbers of lymph nodes with and without metastatic tumour
- The presence or absence of hormone receptors
- The activity of specific enzymes6
Who performs needle biopsies?
In Sweden trained breast radiologists perform the needle biopsy at special breast centres that are breast radiology outpatient clinics, very often located where the mammography screening is done.
In the UK, image-guided, minimally invasive procedures such as ultrasound-guided breast biopsy is most often performed by a specially trained radiologist.5 This varies in different countries of course.
What is the Sentinel Node?
Sentinel node is the first lymph node to which a breast tumour drains lymphatic fluid and metastasis to.7
Why is it important to identify the Sentinel Node?
In the axillary lymph nodes, the lymph is drained from a tumour area. The spread of breast cancer usually occurs to the first lymph node in the armpit.8 This is called the sentinel node. Identification of the sentinel node is therefore an important part of the treatment of breast cancer.8
Why is axillary biopsy performed in breast cancer?
The status of the axillary lymph nodes is one of the most important prognostic factors in patients with breast cancer. Histologic examination of lymph nodes is the most accurate method for assessing lymph node metastasis.9
What is a Sentinel Node Breast Biopsy?
Sentinel node biopsy is a surgical procedure used to determine whether breast cancer has spread beyond a primary tumour into the lymphatic system.10 If the sentinel nodes are free of cancer, then cancer is unlikely to have spread, and removing additional lymph nodes is unnecessary. If a sentinel lymph node biopsy reveals cancer, your doctor might recommend removing more lymph nodes.10
Steps
- Examination
- Diagnostic imaging
- Tissue sampling
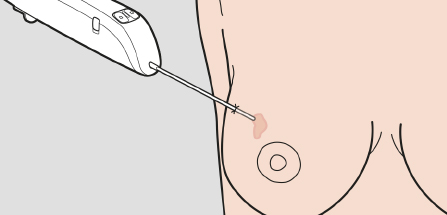
Breast biopsy is a tissue sample from the breast.
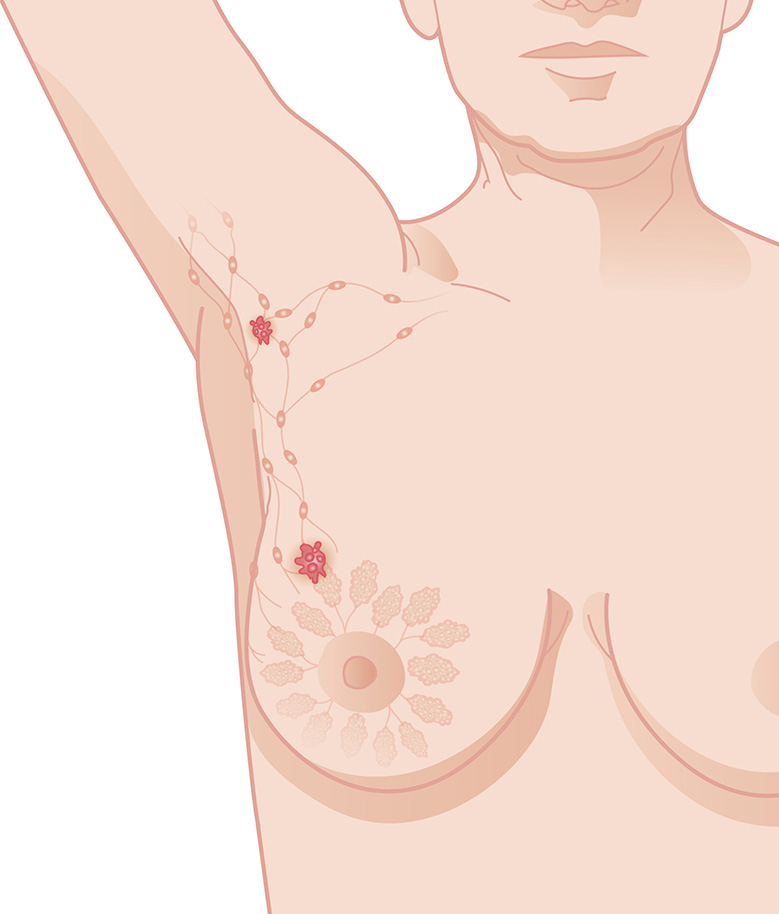
Biopsy of the sentinel node can save patients unnecessary discomfort after surgery.
Referenser
- 1 https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/screening-tests-and-early-detection.html
- 2 https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/breast-cancer/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352475
- 3 https://www.nationalbreastcancer.org/breast-cancer-biopsy
- 4 Nounou MI et al. Breast Cancer: Conventional Diagnosis and Treatment Modalities and Recent Patents and Technologies. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2015;9(Suppl 2):17–34. Published 2015 Sep 27. doi:10.4137/BCBCR.S29420
- 5 https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=breastbius
- 6 Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ, Wang HH, et al. Role of the Surgical Pathologist in the Diagnosis and Management of the Cancer Patient. In: Kufe DW, Pollock RE, Weichselbaum RR, et al., editors. Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine. 6th edition. Hamilton (ON): BC Decker; 2003. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK13237/
- 7 https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantsentinel.html
- 8 https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-sentinel-lymph-node-biopsy-in-breast-cancer
- 9 https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/treatment/surgery-for-breast-cancer/lymph-node-surgery-for-breast-cancer.html
- 10 https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/sentinel-node-biopsy/about/pac-20385264
